Introduction
Chatbots aren’t new. But GenAI-powered chatbots?
That’s a different ball game, especially when deployed securely, scalably, and serverlessly on AWS.
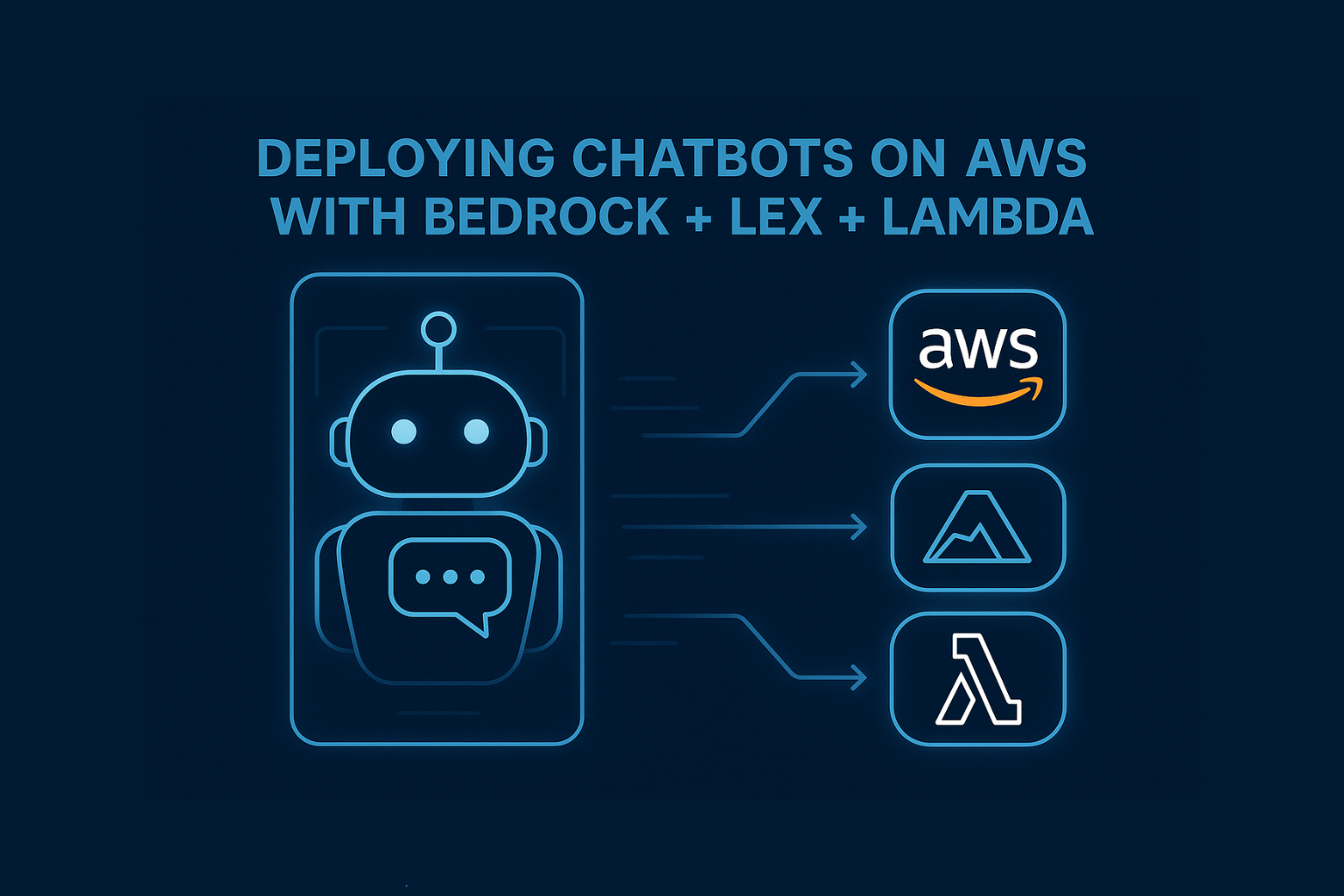
In this guide, we’ll show you how to build and deploy a production-grade chatbot on AWS using:
- Amazon Lex for natural conversation flow
- Amazon Bedrock for LLM responses
- AWS Lambda for orchestration and custom logic
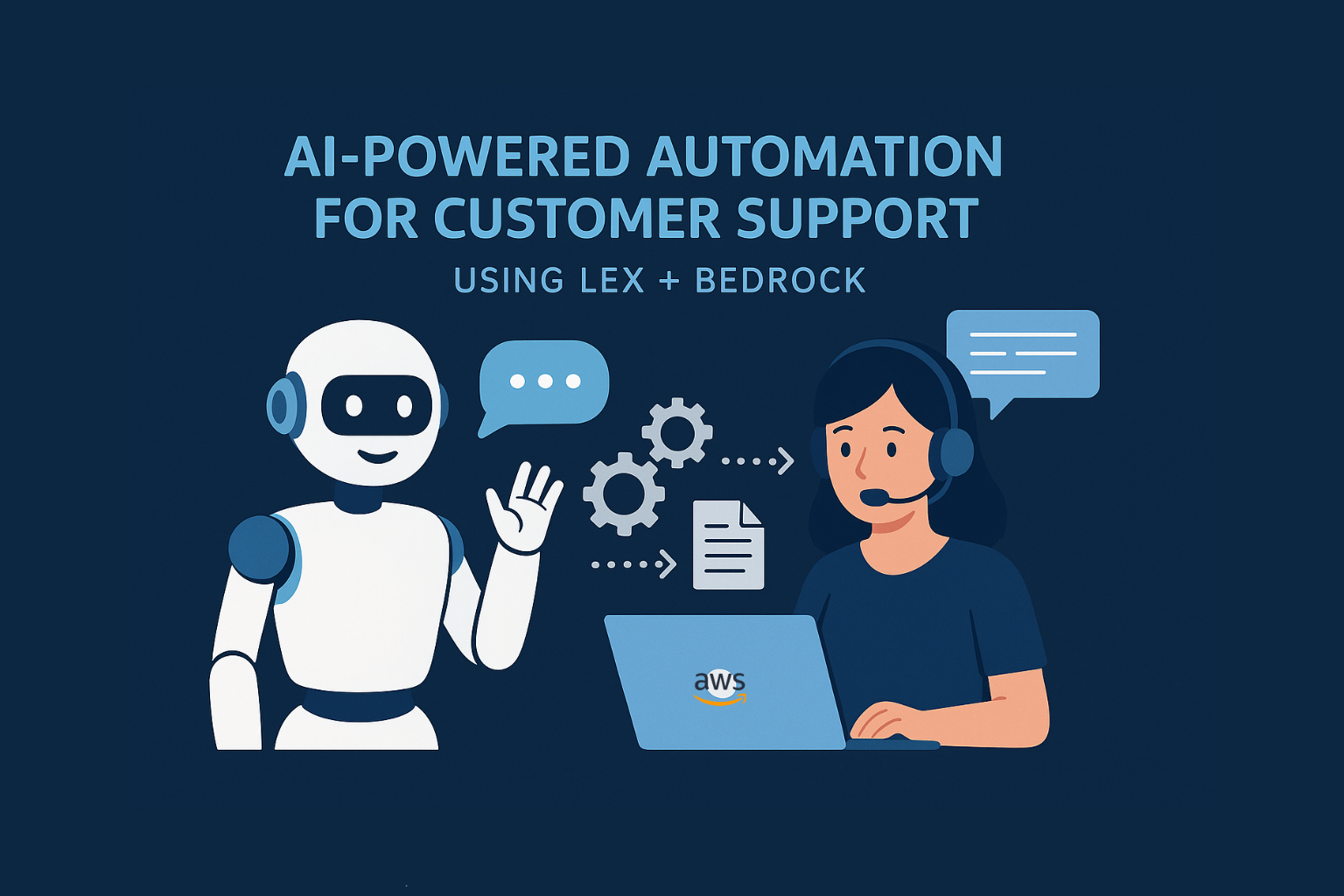
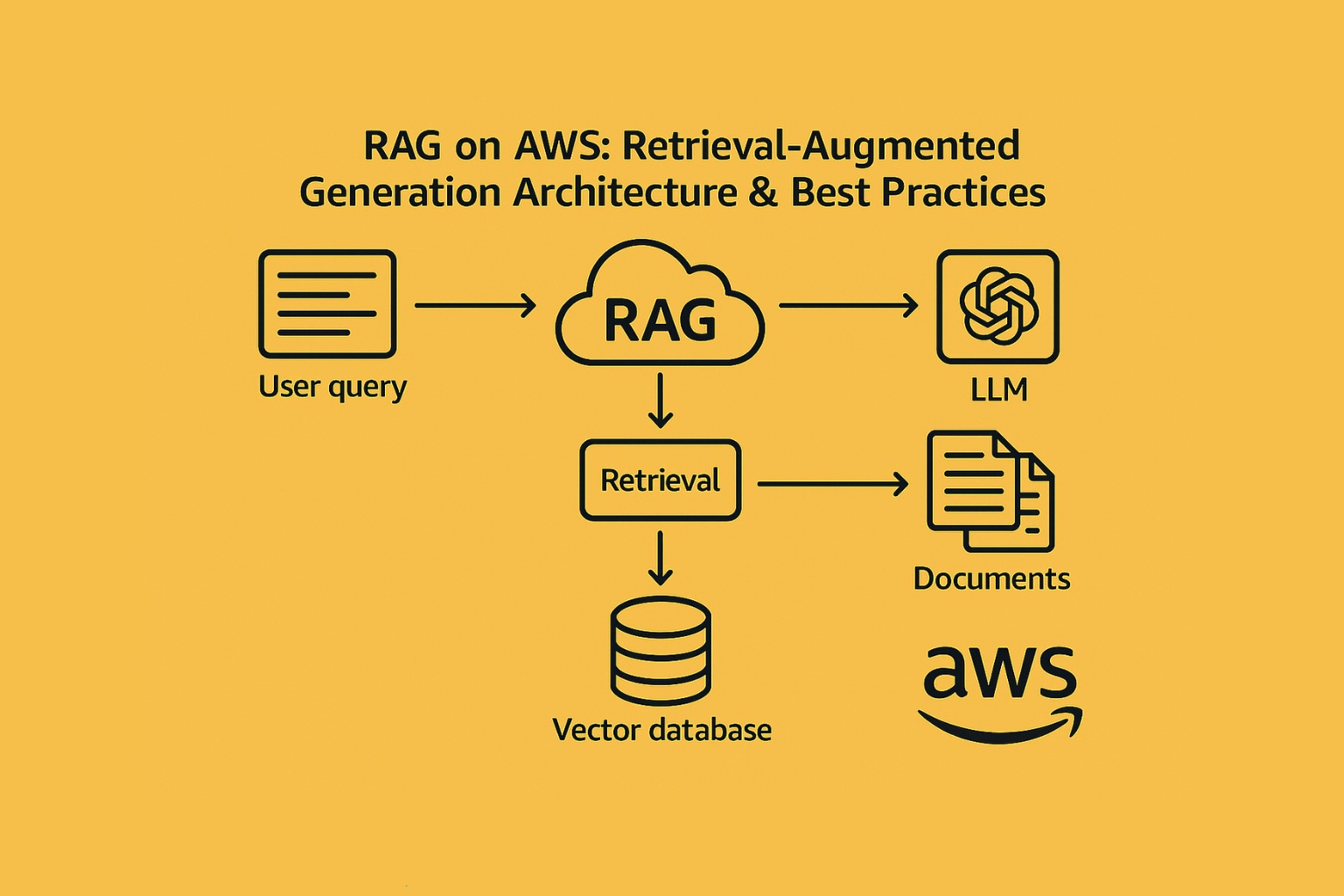
High-Level Architecture
SQL
User → Amazon Lex → AWS Lambda → Amazon Bedrock (Claude/Titan) → Response → Lex → User
Components Breakdown
| Service | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Amazon Lex | Handles speech/text input, dialog state, slot-filling |
| AWS Lambda | Orchestrates the call to Bedrock + post-processes the LLM output |
| Amazon Bedrock | Generates answers from Claude, Titan, or other supported LLMs |
| IAM + VPC + KMS | Enforces security, encryption, and isolation |
Step-by-Step Deployment
1. Design Your Lex Bot
- Define intents like
askQuestion,checkStatus, etc. - Use slots only when necessary (e.g., name, email)
- Connect the Fallback Intent to your Lambda function
2. Build the Lambda Function
This function should:
- Accept the message from Lex
- Construct a prompt (optionally include context)
- Call Bedrock via the AWS SDK
- Return a formatted response
Python
import boto3
bedrock = boto3.client('bedrock-runtime')
def lambda_handler(event, context):
user_input = event['inputTranscript'] prompt = f"Answer as a helpful assistant: {user_input}"
response = bedrock.invoke_model(
body=prompt.encode("utf-8"),
modelId="anthropic.claude-v2"
)
return {
"dialogAction": {
"type": "Close",
"fulfillmentState": "Fulfilled",
"message": {
"contentType": "PlainText",
"content": response.text
}
}
}
3. Connect Lex and Lambda
- In the Lex console, go to Fulfillment
- Attach the Lambda function to your intents
- Test conversations in the Lex test window
4. Secure Your Deployment
- Use KMS if storing user inputs
- Use least-privilege IAM roles
- Set Lambda timeouts and concurrency limits
- Monitor with CloudWatch logs
Optional Enhancements
| Feature | Service |
|---|---|
| Memory/History | DynamoDB or S3 |
| Contextual Search | OpenSearch or RDS (via embeddings) |
| UI Frontend | Amazon Connect, React, or Slack integration |
| Output Control | Bedrock Guardrails or prompt wrapping logic |
| Analytics | CloudWatch Logs + Lex Analytics dashboard |
Ideal Use Cases
- Internal knowledge base assistant
- HR or IT helpdesk chatbot
- Customer FAQ bot
- Lead qualification via conversational forms
Conclusion
You don’t need a full-stack AI team to build an intelligent chatbot.
With Lex + Bedrock + Lambda, AWS enables:
- Natural, conversational interfaces
- LLM-powered intelligence
- Serverless deployment and security baked in
Fast to build. Easy to scale. Ready for production.